 redisson详解
redisson详解
# 1.原来使用redis实现setnx的分布式锁有什么缺陷
- 超时时间设置不当导致并发问题
- 无法实现可重入锁
- 自己编写setnx可能出现bug
- 部分代码如finally中的代码无法保证原子性
锁续命,看门狗
原理:假如我们设置一把锁的过期时间为30s,那么当主线程抢占到锁后,开启一个异步线程,定时扫描过期时间和主线程,如果主线程还没有执行完,就将redis中key重新设置过期时间为30s。
实现:redisson
https://redisson.org/
# 2.Redisson的使用
# 引入jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.6.5</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
# 在springboot中创建客户端配置类
@Bean
public Redisson redisson(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://localhost:6379");
return (Redisson) Redisson.create(config);
}
2
3
4
5
6
核心api
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockName);//获取一把锁
lock.lock(); //加锁
lock.unlock();//释放锁
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //占用多少秒后释放
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//尝试获取锁,如果100s内没获取到则返回false,若成功获取则10s删除锁
2
3
4
5
# 执行流程简析
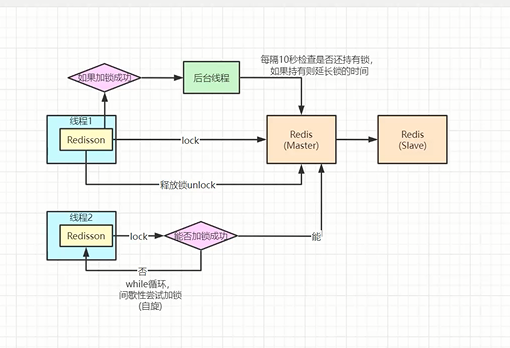
一台机器中的线程1和另外一台机器的线程2准备抢占锁,若线程1抢占成功
- 线程1会开启另一个线程,每隔10s检测线程1是否还持有锁,如果持有就延长锁时间
- 线程2通过while+阻塞自旋间歇性尝试加锁
# 3.源码分析
# ①先看lock源码
public void lock() {
try {
this.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
this.lockInterruptibly(-1L, (TimeUnit)null);
}
//核心:
//leaseTime :释放锁时间
public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
//尝试获得锁:看详情1
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId); //重点
//如果不为空,,则表示抢占锁失败
if (ttl != null) {
//请看详情3讲解
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
while(true) {
//再次尝试获取锁
ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
//获取锁失败,则进行阻塞
if (ttl >= 0L) {
//这里使用了semphere信号量机制进行线程的阻塞
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
this.getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
//获取锁成功了,这里就取消当前线程订阅的管道
this.unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
详情1
private Long tryAcquire(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
return (Long)this.get(this.tryAcquireAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
//返回的是个Tuture对象
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
//真正获取锁逻辑:看详情2
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
//给Tuture加上监听器,一旦获取结果则调用此方法
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
//如果执行成功
if (future.isSuccess()) {
Long ttlRemaining = (Long)future.getNow();
//表示获取锁成功
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
//开启线程定期锁续命:详情3
RedissonLock.this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
详情2
//真正获取锁逻辑
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
this.internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command, "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end; return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", Collections.singletonList(this.getName()), new Object[]{this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
2
3
4
5
//KETS[1] : 锁的名字
//ARGV[1] : 超时时间leaseTime,其实是lockWatchDogTime 默认30s
//ARGV[2] : 线程id
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then //如果当前锁没有被任何线程占有
redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); //使用hash的结构创建锁 key(锁名) field(线程) value(重入次数)
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); //设置过期时间,默认30s
return nil; //设置成功则返回null
end;
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then //如果被占有的锁的线程是当前线程,即执行可重入了逻辑
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); //可重入+1
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; //在次设置过期时间30s
end;
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]); //如果没有成功获取锁,则返回该锁剩余的过期时间
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
详情3
锁续命逻辑:scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId)
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(final long threadId) {
if (!expirationRenewalMap.containsKey(this.getEntryName())) {
Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
//只要线程成功获取了锁,就会执行这里的逻辑
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
//查看这把锁对应的线程有没有被释放或过期,没有的话,则重新设置为30s,并返回1;
RFuture<Boolean> future = RedissonLock.this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(RedissonLock.this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN, "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return 1; end; return 0;", Collections.singletonList(RedissonLock.this.getName()), new Object[]{RedissonLock.this.internalLockLeaseTime, RedissonLock.this.getLockName(threadId)});
//future监听
future.addListener(new FutureListener<Boolean>() {
public void operationComplete(Future<Boolean> future) throws Exception {
RedissonLock.expirationRenewalMap.remove(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName());
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", future.cause());
} else {
//如果续命成功,则通过递归的方式进行下一轮定时任务
if ((Boolean)future.getNow()) {
RedissonLock.this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
});
}
//这里可以看出来,每个10s执行一次
}, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (expirationRenewalMap.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), task) != null) {
task.cancel();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
详情3
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
2
首先,线程没有获取锁成功,这里会根据redis中的消息队列机制,让当前一个线程去订阅一个通道channelRFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
当通道channel中有消息时,线程可以执行特定的方法:this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
//订阅了通道chennel且channel收到数据后,就会执行以下方法
protected void onMessage(RedissonLockEntry value, Long message) {
if (message.equals(unlockMessage)) {
//从信号量中的进行唤醒线程
value.getLatch().release();
//不重要
while(true) {
Runnable runnableToExecute = null;
synchronized(value) {
Runnable runnable = (Runnable)value.getListeners().poll();
if (runnable != null) {
if (value.getLatch().tryAcquire()) {
runnableToExecute = runnable;
} else {
value.addListener(runnable);
}
}
}
if (runnableToExecute == null) {
return;
}
runnableToExecute.run();
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
以上可以看出,必须要管道中收到了消息,这里才可以唤醒AQS队列中沉睡得的线程,这就要引出unlock了
# ②unlock
public void unlock() {
Boolean opStatus = (Boolean)this.get(this.unlockInnerAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
if (opStatus == null) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: " + this.id + " thread-id: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
} else {
if (opStatus) {
this.cancelExpirationRenewal();
}
}
}
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return this.commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(this.getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN, "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); return 1; end;if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then return nil;end; local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); if (counter > 0) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); return 0; else redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); return 1; end; return nil;", Arrays.asList(this.getName(), this.getChannelName()), new Object[]{LockPubSub.unlockMessage, this.internalLockLeaseTime, this.getLockName(threadId)});
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
//KEYS[1] 锁名字
//KEYS[2] 通道名
//
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then //锁是否存在
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); //若不存在,可能是过期了,这时需要向通道channel发布消息
return 1;
end;
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then //如果锁的线程不是当前线程所占有的,表示当前线程尝试删除别人的锁,直接返回null
return nil;
end;
local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); //让当前线程重入次数-1
if (counter > 0) then
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); //如果锁的重入次数没有到0,表示锁继续被占有,这里进行一次锁续命
return 0;
else redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); //表示重入次数为0,则直接删除
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); //向通道发送信息
return 1;
end;
return nil;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
从上面可以看出redisson采用订阅发布机制+AQS实现阻塞线程的唤醒。
- 加锁:redis 中设置 hash 结构,默认过期时间为 30000ms。
- 维持加锁:后台有一个调度任务,每10秒钟调度一次,只要客户端和key 都还存在,就会刷新当前 key 的过期时间。
- 锁互斥:别的客户端或者别的线程再来加锁,会陷入 while(true) 的死循环中,等待。
- 可重入锁:同一个线程可以加锁多次,每次的话,就是在 hash 结构上自增1。
- 手动释放锁:在 hash 结构上递减1,对比剩余个数是否为0,为0则直接删除 key。
- 宕机释放锁:当客户端宕机之后,后台的调度任务就会取消,key 的过期时间就不会在被刷新,默认30s后,key 自动消失。
- 尝试加锁超时:在循环中,一直尝试获取锁,若时间到了之后,还没有获取到,就退出循环,返回 false。
- 自动释放锁:在加锁的时候,设置超时时间,这样就不会有调度任务,key 会在设置的过期时间之后过期。
# ③默认非公平锁
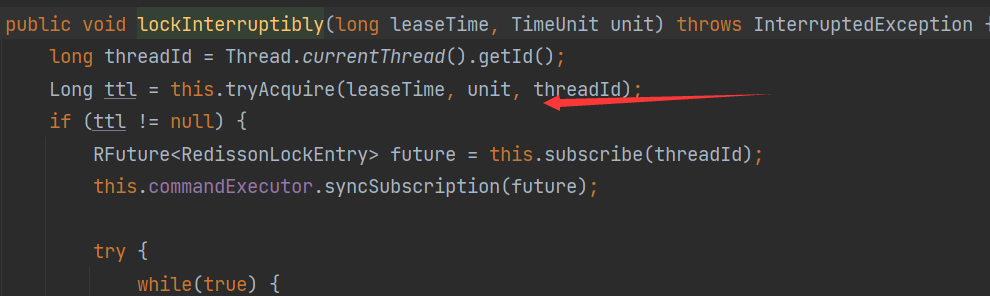
调用lock方法,线程以上来就尝试获取锁,可以看出是非公平锁。当然在redisson中也有公平锁的实现
什么时候锁会释放?
- 宕机,看门狗机制无法执行,redis中数据自动过期
- 主动调用unlock
# ④默认可重入锁
从之前的lua脚本很容易看出来redisson采用hash结构来实现可重入锁
# ⑤boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
redisson 提供了一个高阶用法,这个就是说,尝试100s,如果100s还获取不到锁就放弃;如果获取到锁,只会占有这个锁 10s , 如果 10s 还没有释放锁,就会自动进行释放。
- 注意:看门狗和锁续命是没有手动设置过期时间、调用lock方法才会有的一个特殊功能,如果调用trylock,就可能不会使用锁续命和看门狗机制。
# ⑥公平锁等等
TODO
参考:
https://juejin.cn/post/6901951315962757134#heading-10 (opens new window)
# 4.Redis主从架构锁失效问题
为了提高锁的可用性,使用主从架构下
但是在主从架构下会有问题:
如图所示,如果process1尝试去获取锁,并获取master锁成功,立即返回给process1。然后正准备将数据同步给slave,此时master挂了,slave当选新结点,但是其中没有锁信息,因为之前master还未同步就挂了。此时process2来获取锁,发现master可获取锁。最终导致锁失效。
其主要原因是因为redis是一种AP架构,其保证可用性,但是在一致性方面有些欠缺。
# 那怎么解决呢?
- 使用zookeeper作为分布式锁
zookeeper也可以做为分布式锁,其是CP架构,保证了数据的一致性,当process1向zookeeper集群中的leader请求锁时,只有当zookeeper集群中超过半数的结点同步了信息后,leader才会返回信息给process1。这样就算leader挂了,zookeeper集群也会选择同步数据最多的结点当选新leader,而新leader中一定有锁信息,process2就无法获取锁。
但是呢实际上公司大多数用redis作为分布式锁。因为zookeeper作为分布式锁,其请求锁时保证集群半数结点同步数据成功,这个过程是非常耗时间的,非常影响性能。
- redlock方案
其实底层也是借鉴了zookeeper的半数机制概念。
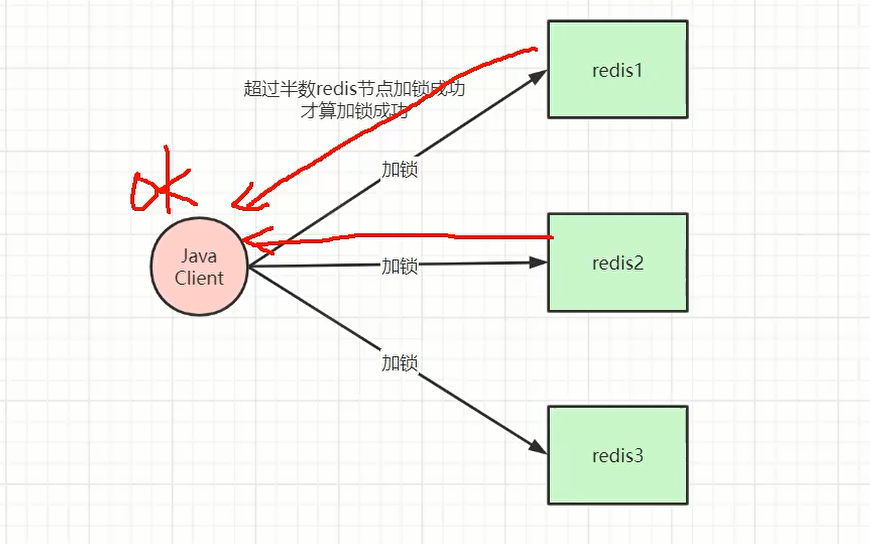
三个redis结点是对等的。建立锁时,要超过半数以上的结点成果获取锁(相比于zookeeper效率高),才返回获取所成功信息。否则获取锁失败。
但是实际上,这种方案也是不建议使用的。
- 高可用问题
上述的是3个单节点,那么如果超过半数以上结点挂了,整个集群就没了。所以我们会考虑主从架构问题,让每个结点再拉一个slave。
但是这是有问题的。
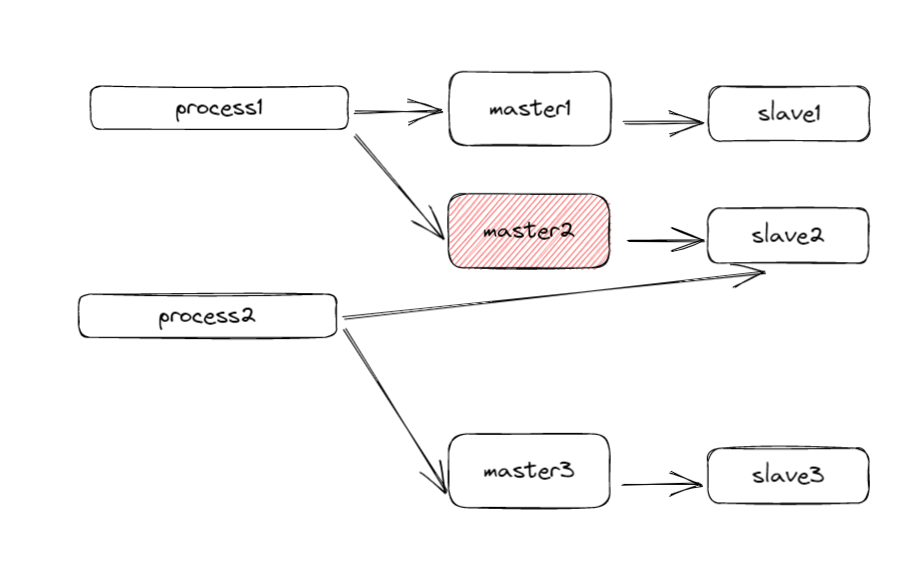
如图所示,如果process1成功在master1、master2上成功加锁,当slave2还没有成功获取数据时,此时master2宕机,即选举新结点slave2作为新master,此时process2来获取锁,因为新的master2没有之前的锁信息,process2成功再master3和master2上加锁成功,固造成锁失效问题。
其实也就重现了redisson那个主从问题
那怎么办呢?不加slave,我们多加几个master吧,设置20个,总不会挂10个吧。确实可以,但是要考虑性能问题,redis加锁要加十个以上,加这么做锁不直接退化成了zookeeper低效率了吗。我们使用redis就是为了高性能,这样我们还不如使用zookeeper呢?
- 持久化问题
通常我们aof持久化都是选用everyseconds每秒存储到aof文件。但是这样可能会丢失1s的数据。
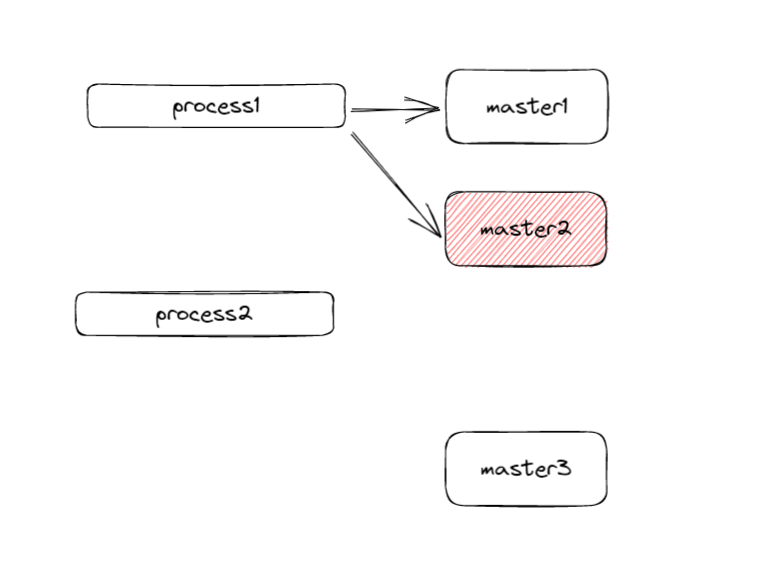
如图,当process1在master1和master2加锁成功,那么在master2还没有持久化时(没过1s),突然宕机,然后又重启,此时master2上是没有锁信息的,这时process2成功在master2和master3上加到数据。固锁失效
所以redlock的问题非常多,不建议高并发下使用。
至今,redis作为分布式锁还没有完全正确的方案。
# 5.分布式锁怎么进行优化
加锁本质:并行变串行
与高并发架构有违背
优化方向
锁的粒度:锁的粒度越小,性能会提高
使用分段锁
比如银行系统
一个用户账户有1000元。此时一个用户发起转账。
我们一般我设置一个锁user_account锁锁住这个账户,然后进行扣款,那么这肯定就是一段时间内只有一个线程可以扣款这个用户。效率可能比较低
如果使用分段锁呢?
我们将1000元 - user_account分段为
100 - user_account_1
100 - user_account_2
100 - user_account_3
………………
100 - user_account_10
这样每次扣款,就可以通过一定的算法定位线程该去获取哪一把锁,只要扣减后不小于0,就扣款成功,否则回去下一把锁,这样的情况下,在有很多次用户扣款请求下,就会有10个线程并行去运行。
当然,我们应该将数据取到内存,在将其分为100、100多分这样才可以。
比如 key value
user_account_1:100
user_account_2:100
user_account_5:66
……
每次扣减在缓存中进行,最后当业务结束,在异步进行累加后保存到数据库
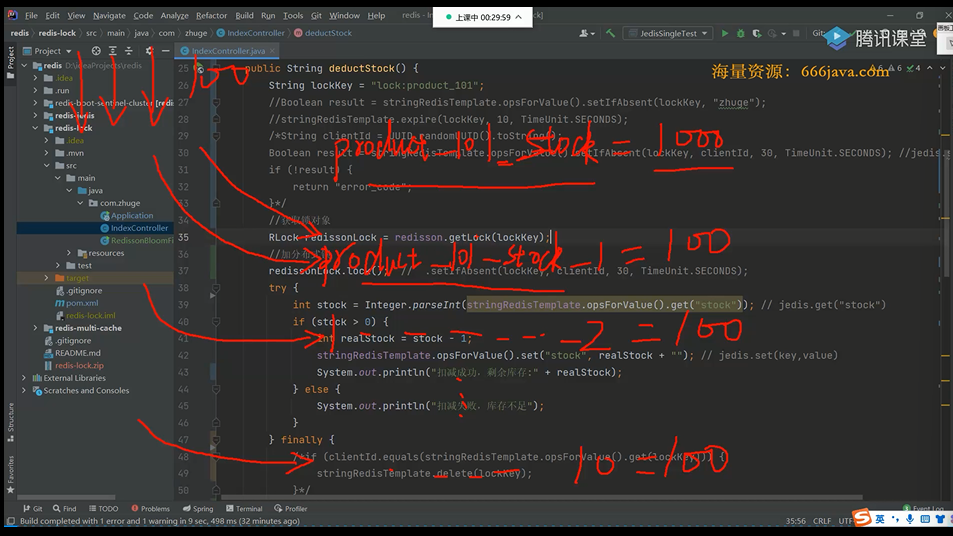
类似ConcurrentHashMap底层就有分段锁,可以参考下1.7,1.8锁粒度更细
锁优化的参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/86935799
https://blog.csdn.net/hbtj_1216/article/details/77161198