 常见的排序算法
常见的排序算法
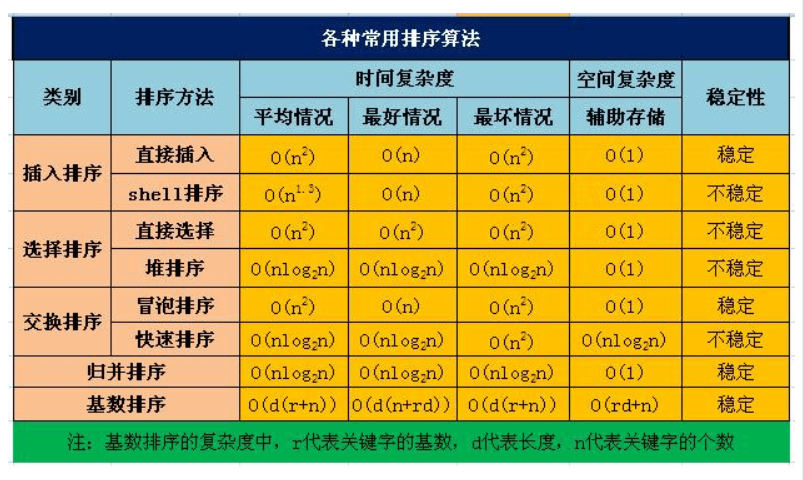
# 插入排序
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] arr=new int[]{5,4,7,2,9,10};
solution.insertSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void insertSort(int[] arr){
int len=arr.length;
if(len<=1) return ;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
int j=i-1;
int temp=arr[i];
while(j>=0&&arr[j]>temp){
arr[j+1]=arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 希尔排序
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] arr = {5, 4, 7, 2, 8, 3};
solution.shellSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void shellSort(int[] arr) {
int length = arr.length;
for (int step = length / 2; step >= 1; step /= 2) {
for (int i = 0; i < step; i++) {
for(int j=i+step;j<arr.length;j+=step){
int k=j-step;
while(k>=0&&arr[k]>arr[k+step]){
swap(arr,k,k+step);
k-=step;
}
}
}
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int a,int b){
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
另外一种写法
class Solution {
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
shellSort(nums);
return nums;
}
public void shellSort(int[] nums){
int len=nums.length;
for(int step=len/2;step>=1;step/=2){
for(int i=0;i<step;i++){
shellSelect(nums,step,i);
}
}
}
public void shellSelect(int[] nums,int step,int i){
for(int j=step+i;j<nums.length;j+=step){
int curNum=nums[j];
int pre=j-step;
while(pre>=0&&nums[pre]>curNum){
nums[pre+step]=nums[pre];
pre-=step;
}
nums[pre+step]=curNum;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 选择排序
class Solution {
//写一个选择排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr=new int[]{4,3,7,2,9,5,2,5};
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.selectSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void selectSort(int[] arr){
for(int i=0;i<arr.length-1;i++){
int min=i;
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++){
if(arr[min]>arr[j]){
min=j;
}
}
if(min!=i){
swap(arr,min,i);
}
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr,int a,int b){
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
为什么选择排序是不稳定的? 假设原始数组为 [4, 3, 2, 4*, 1],其中数字4*表示与前面的4是相等的元素。选择排序的过程如下:
在第一趟选择中,会选择最小的元素1,将其与第一个位置的4交换,数组变为 [1, 3, 2, 4*, 4]。 接下来,在第二趟选择中,会选择第二小的元素2,将其与第二个位置的3交换,数组变为 [1, 2, 3, 4*, 4]。 继续进行选择排序,最终得到排序后的数组 [1, 2, 3, 4, 4*]。 在这个排序过程中,原始数组中的两个相等的4被交换了位置,这破坏了它们的相对顺序。因此,选择排序不是稳定的排序算法。
# 堆排序

public class Main {
//手写一个堆排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5,4,6,1,2};
Main main = new Main();
main.heapSort(arr);
System.out.println(arr);
}
public void heapSort(int[] arr) {
int len = arr.length;
if (len <= 1) {
return;
}
buildHeap(arr, len);
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
swap(arr, 0, i);
len--;
heapify(arr, 0, len);
}
}
private void buildHeap(int[] arr, int len) {
for (int i = len / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, i, len);
}
}
private void heapify(int[] arr, int index, int len) {
while (true) {
int maxPos = index;
if (index * 2 + 1 < len && arr[index * 2 + 1] > arr[index]) {
maxPos = index * 2 + 1;
}
if (index * 2 + 2 < len && arr[index * 2 + 2] > arr[maxPos]) {
maxPos = index * 2 + 2;
}
if (maxPos == index) {
break;
}
swap(arr, index, maxPos);
index = maxPos;
}
}
private void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
public void heapInsert(int[] arr,int index){
while(arr[index]>arr[(index-1)/2]){
swap(arr,index,(index-1)/2);
index=(index-1)/2;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# 冒泡排序
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] arr=new int[]{5,4,8,2,9,1,2};
solution.bubbleSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void bubbleSort(int[] arr){
int len=arr.length;
if(len<=1) return;
for(int i=0;i < len; i++){
for(int j=0;j<len-i-1;j++){
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){
swap(arr,j+1,j);
}
}
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr,int a,int b){
int temp=arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 快速排序
时间复杂度 nlogn
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{4,3,7,8,1,2,1};
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.quickSort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void quickSort(int[] arr,int left,int right){
if(left>right) return;
int partition =partition(arr,left,right);
quickSort(arr,left,partition-1);
quickSort(arr,partition+1,right);
}
public int partition(int[] arr,int left,int right){
//随机性
Random random =new Random();
int RandomIndex = left + random.nextInt(right - left + 1);
swap(nums, left, RandomIndex);
int partition = left;
int i=left,j=right;
while(i<j){
while(i<j&&arr[j]>=arr[partition]) j--;
while(i<j&&arr[i]<=arr[partition]) i++;
if(i<j){
swap(arr,i,j);
}
}
swap(arr,left,i);
return i;
}
public void swap(int[] arr,int a,int b){
int temp = arr[a];
arr[a]=arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 归并排序
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 5, 8, 1, 2, 4, 5};
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.mergeSort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public void mergeSort(int[] nums,int left,int right){
if(left>=right) return;
int mid=(left+right)/2;
mergeSort(nums,left,mid);
mergeSort(nums,mid+1,right);
merge(nums,left,right,mid);
}
public void merge(int[] nums, int left, int right, int mid) {
int[] temp=new int[right-left+1];
int lPos=left,rPos=mid+1,index=0;
while(lPos<=mid&&rPos<=right){
if(nums[lPos]<nums[rPos]){
temp[index++]=nums[lPos++];
}else{
temp[index++] = nums[rPos++];
}
}
while(lPos<=mid) temp[index++]=nums[lPos++];
while(rPos<=right) temp[index++] = nums[rPos++];
for(int i=0;i<temp.length;i++){
nums[left+i]=temp[i];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 基数排序
public class RadixSort {
// 获取数组中的最大值
private static int getMax(int[] arr) {
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
// 基数排序
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
int max = getMax(arr); // 获取数组中的最大值
int exp; // 位数
for (exp = 1; max / exp > 0; exp *= 10) {
countingSort(arr, exp);
}
}
// 计数排序
private static void countingSort(int[] arr, int exp) {
int[] output = new int[arr.length];
int[] count = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(count, 0);
// 统计每个位上的数字出现次数
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++;
}
// 计算累积次数
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// 构建排序后的数组
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i];
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--;
}
// 将排序后的数组复制到原始数组
System.arraycopy(output, 0, arr, 0, arr.length);
}
// 测试基数排序算法
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66};
System.out.println("原始数组: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
radixSort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后数组: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2024/02/22, 14:03:19